[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) with extremely high spatial resolution allows people to clearly see the electromagnetic radiation emitted near the black hole's horizon for the first time, and the shadow inside the radiation ring is the most direct black hole at present. Evidence of theoretical concepts. The data from this observation are widely used to further verify general relativity and black hole physics, and to study physical processes under extreme conditions. In September of the same year, the EHT team won the $ 3 million breakthrough award in basic physics.
In a recent study, the team of Shu Jing, a researcher at the Institute of Theoretical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Yuan Qiang, a researcher at the Zijinshan Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and their collaborators pointed out that the horizon telescope has not only brought landmark progress to astrophysics. Polarization data is also expected to explore the existence of ultralight axon dark matter, which will have a profound impact on the field of particle physics.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a project that aims to observe supermassive black holes in the center of galaxies. The plan combines very long baseline interference technology (VLBI) with radio telescopes around the world, and uses eight radio telescopes distributed in many parts of the world to jointly observe the same target source and record data to form a virtual telescope with a caliber equivalent to the diameter of the earth. The angular resolution of the telescope is increased to an extent sufficient to observe the scale structure of the event horizon. The event horizon telescope is expected to use this to test whether Einstein's general theory of relativity will produce deviations under the strong gravitational field near black holes, study the accretion disks and jets of black holes, explore the existence of event horizons, and develop basic black hole physics.
According to the predictions of the general theory of relativity, if there is a sufficiently light boson, and its Compton wavelength and black hole horizon radius are on the order of magnitude, its wave function will be continuously enlarged around the rotating Cole black hole. These particles extract energy from the black hole's rotation, forming a Bose cloud surrounding the black hole. This process is called superradiation. The system of rotating black holes and Bose clouds is like a "gravitational atom". The nucleus is a rotating black hole, and the interaction is gravity.
A boson is a particle that has an integer spin quantum number following Bose-Einstein statistics. Bosons do not follow the Pauli exclusion principle, multiple isotactic bosons can be in the same quantum state at the same time, and Bose-Einstein condensation can occur at low temperatures. The opposite of bosons is fermions. Fermions follow Fermi-Dirac statistics. The spin quantum number is a half integer (1/2, 3/2, ...). The basic structure of matter is fermions, while the basic interactions between matter are transferred by bosons.
It is worth mentioning that this superradiation process is not sustainable. It is widely considered that after the sufficient angular momentum of the black hole is extracted, the remaining black hole rotation energy is not sufficient to continue the superradiation process. The assumption in this case is that the interactions between bosons are small enough that they can always be ignored in superradiation. When the self-interaction of the boson is strong enough, the energy density of the Bose cloud will have an upper limit, after which gravitational atoms will collapse. This violent process is called Bose Nova, and its name comes from the condensed matter laboratory. Collapse of Bose-Einstein condensation. The collapsed gravitational atoms will throw out the light particles in the outer layer, and then the superradiation process will start again. This periodic process keeps the light particles near the black hole's horizon in a high density state. The aperture position r_ring seen by the horizon telescope is near the r_max where the density of the Bose cloud is high.
How to find these axons that may be attached to the black hole? The non-relativistic axons generated by superradiation can be regarded as a coherent field, and the wave function oscillates with time. If this coherent field is coupled with the standard model, it will be found that some parameters of the standard model will also have very small oscillations. As an axon scalar, the axion corresponds to the observing measurement in the parity transformation to the odd transformation, such as the neutron electric dipole moment oscillation caused by the axon-gluon coupling. In addition to coupling with strong acting gluons, axons can also naturally interact with electromagnetic fields. If a beam of polarized light is radiated from an axon cloud, its polarization angle will oscillate accordingly. Its amplitude depends on the axon density at the point where the radiation is emitted, making the high-speed rotating black hole the target for axon detection.
Axion is a kind of subatomic particle that exists in nature to predict 'existence' in particle physics and celestial particle physics and condensed matter physics. Nowadays, particle physics scientists in China have 'discovered' and confirmed that the axion is the reality of nature itself. Particles (Legend). In nature, the energy spectrum of axon particles is the mass of linear particle equations in one dimension in space. Axion particles are a kind of 'secondary' particles after super-symmetric particle collision with positron and electron collision. They are also in Bose. A new polarized particle "repulsion" of the energy level of 'diffraction + radiation' at the sub-energy level and 'escape'. Axion particles use a kind of energy axis extending 'one-dimensional time and space' to perform linear transition angular momentum motion. Axion particles can also be understood as trajectory transitions of 'magnetic monopole particles' which can be physically measured and observed. The intrinsic state of axon particles is strongly related to the existence of dark matter particles in 'dark matter'. Axon particle's repulsive repulsive unipolar characteristics determine that it can only do one-dimensional linear equations of repulsive force movement, so the concept of axon particles is strongly related to 'magnetic unipolar particles' neutrino particles' and' dark matter ' A collective term for particles `` repulsors ''.
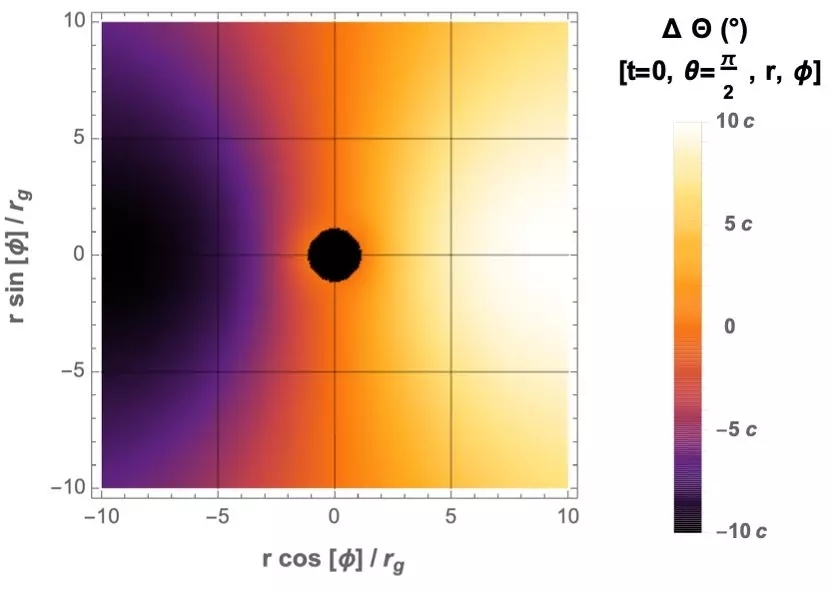
In addition to time oscillations, it is also possible to compare the oscillations of the deflection angles of radiation at different positions. Because the Bose cloud generated by superradiation carries the same angular momentum as the rotation direction of the black hole, its wave function will also have a phase difference in the longitude angle of the black hole: the amplitude of the deflection angle oscillation at different positions can also be used to analyze the Bose cloud system Distribution of energy density.
At present, the observation telescope has not published observation data of the polarization angle. In past observations, the sub-observatory of the cooperation group has shown that it can have observation accuracy of 3 degrees. The researchers take this as the criterion and look forward to the limit that the joint observation group can achieve in the future on the parameter space of the axons, and find that it will be many orders of magnitude higher than the existing limit.
Source: Institute of Theoretical Physics, Encyclopedia
Stainless Steel Plate,316 Stainless Steel Plate,304 Stainless Steel Plate,Stainless Steel Plate Covers
Shandong Jianlong Steel Co. , https://www.jianlongmetal.com
